Unnatural amino acid incorporation technology
Technology
Platform Technology Introduction
Conventional TechnologyLysine Conjugation

Random conjugation results in structural deformation in protein
Decreased protein activity
Difficulty in manufacturing homogenous drugs
Complicated purification process
Our TechnologySite-specific Bioconjugation

Site-specific conjugation minimizes deformation of protein structure
Maintains protein activity
Allows manufacturing of homogenous drugs
Simple purification process
UAA (Unnatural amino acid) containing click chemistry reactive handle
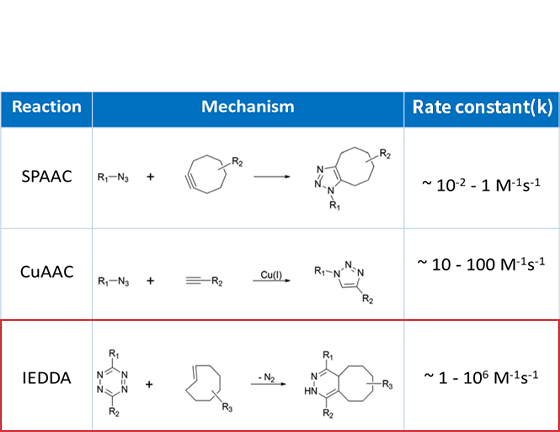
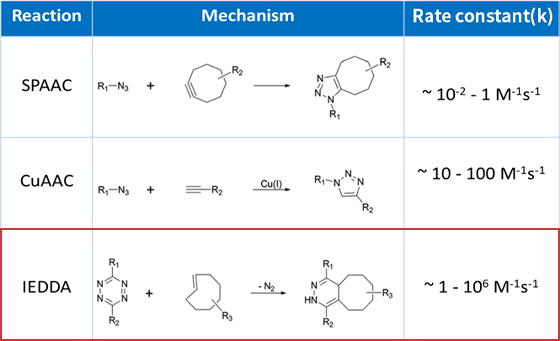
IEDDA is the fastest click chemistry reaction, which involves the reaction between tetrazine and trans-cyclooctene (TCO) The rapid and efficient formation of a covalent bond between two molecules under mild and biocompatible conditions Unnatural amino acids are used to introduce new chemical and physical properties to proteins.

Engineered orthogonal pair of tRNA
/ aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
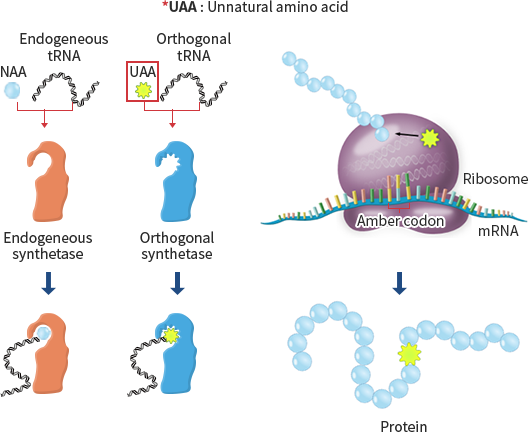
Orthogonal pair of Methanococcus jannaschii tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (MjTyrRS) and its cognate suppressor tRNA (MjtRNATyrCUA) has been developed for UAA incorporation into proteins.
IEDDA click chemistry reaction
Therapeutic drug
incorporated unnatural amino acids
Linker-Albumin
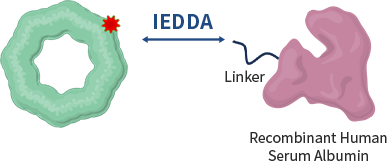
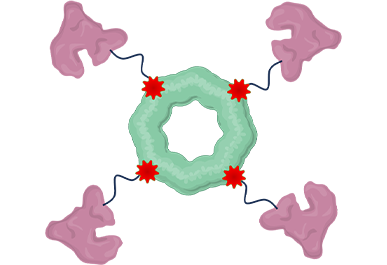
Rapid reaction through click chemistry(IEDDA) High safety due to site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acid High conjugation yield achieved through fast reaction and enable simple manufacturing process

Drug-Albumin Conjugate
Evolution of bioconjugation technology
-
Recombinant Protein
Very short half-life
- · Protein from genetic recombination technology
- · Short half-life in vivo
- · Decreased stability in vivo
-
Fusion Protein

Short half-life,
Non-site-specific- · Expressed as fusion partner protein
- · Unable to site-specifically conjugate drugs
- · Potential risks in immunogenicity
- · Potential side effects due to high dose administration following decreased activity
-
PEGylation
Achieve certain half-life extension
- · Increase stability by random conjugation of PEG polymers
- · Decreased activity due to PEG
- · Potential immunogenicity due to PEG
-
Fc Conjugation
Risks of side effects
- · Long-acting drugs by conjugation with Fc region
- · Application limited to certain drug moiety due to non-specific conjugation
- · Decreased manufacturing yield and difficulties in CMC management due to non-specific conjugation
- · Potential side effects due to FC region
-
SelecAll™ Technology
Increase half-life and minimize side-effects
- · Development of long-acting drugs by conjugating albumin into a specific site
- · Minimize reduction of drug activity
- · Increase half-life and minimize side effects
- · High production yield and simple CMC management
- R
e
c
o
m
b
i
n
a
n
t
P
r
o
t
e
i
n - F
u
s
i
o
n
P
r
o
t
e
i
n - P
E
G
y
l
a
t
i
o
n - F
c
C
o
n
j
u
g
a
t
i
o
n - S
e
l
e
c
A
l
l
™
T
e
c
h
n
o
l
o
g
y
-

Very short half-life
- · Protein from genetic recombination technology
- · Short half-life in vivo
- · Decreased stability in vivo
-

Short half-life, Non-site-specific
- · Expressed as fusion partner protein
- · Unable to site-specifically conjugate drugs
- · Potential risks in immunogenicity
- · Potential side effects due to high dose administration following decreased activity
-

Achieve certain half-life extension
- · Increase stability by random conjugation of PEG polymers
- · Decreased activity due to PEG
- · Potential immunogenicity due to PEG
-

Risks of side effects
- · Long-acting drugs by conjugation with Fc region
- · Application limited to certain drug moiety due to non-specific conjugation
- · Decreased manufacturing yield and difficulties in CMC management due to non-specific conjugation
- · Potential side effects due to FC region
-

Increase half-life and minimize side-effects
- · Development of long-acting drugs by conjugating albumin into a specific site
- · Minimize reduction of drug activity
- · Increase half-life and minimize side effects
- · High production yield and simple CMC management
Convential bioconjugation techniques
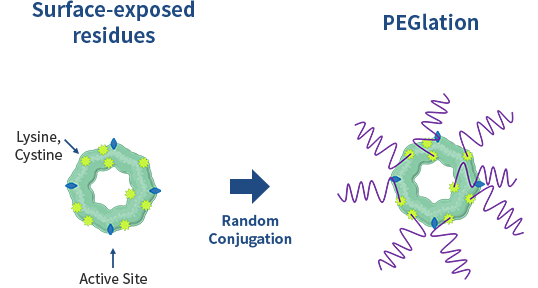
Random conjugation results in structural deformation in protein Decreased protein activity Difficulty in manufacturing homogenous drugs Complicated purification process
Site-specific Bioconjugation techniques
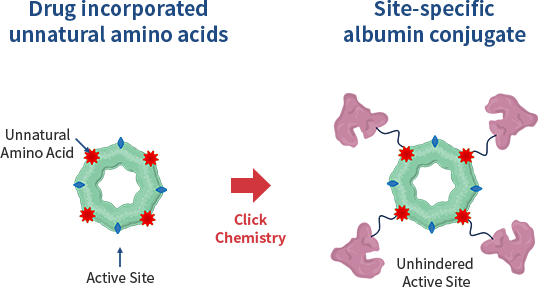
Site-specific covalent conjugation retains original protein structure and biological activity, leading to high conjugation yields (>90%) with homogeneous drug preparation